https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ZQ4y1f7go/?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0
自旋锁
操作系统等待队列 win32 event/ linux futex
- 系统调用
- 线程切换
多核、占用锁时间短,通过自旋,消耗更小,防止线程切换 单核、占用锁时间长,通过等待队列更合适
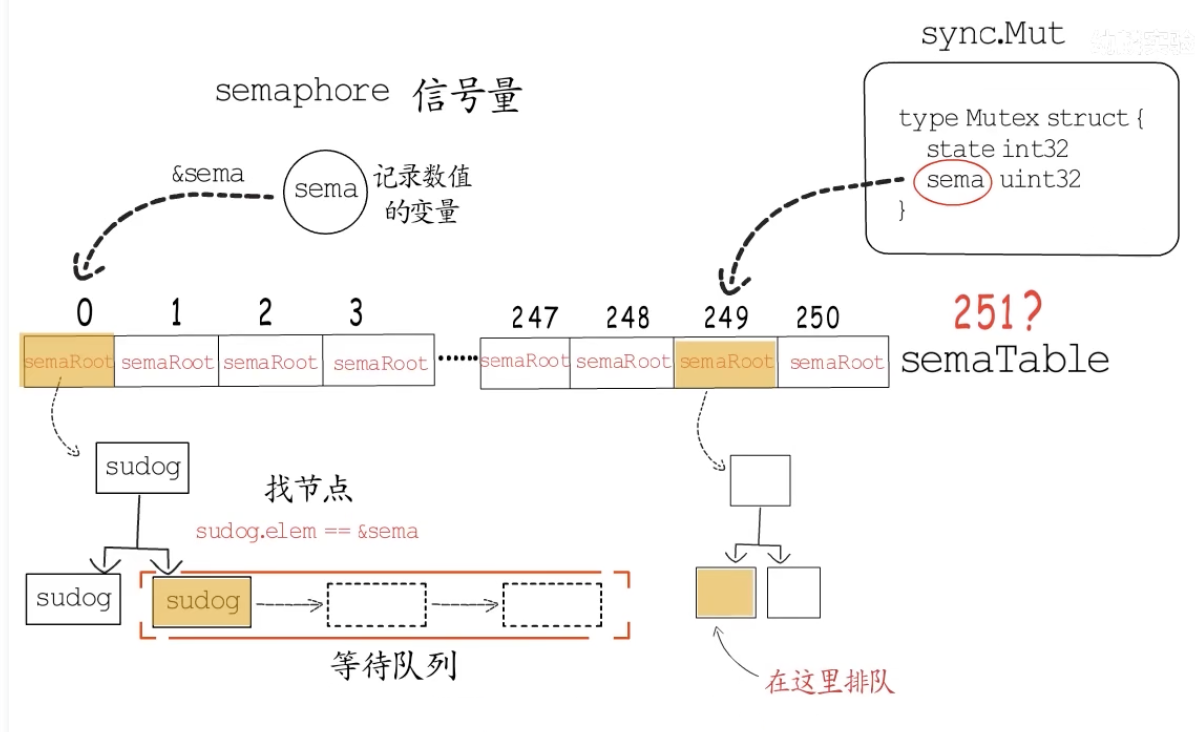
go 中的等待队列 semaphore 供协程使用的信号量
sematable 存储 251 棵平衡树根
acquire #
// Called from runtime.
func semacquire(addr *uint32) {
semacquire1(addr, false, 0, 0, waitReasonSemacquire)
}
func semacquire1(addr *uint32, lifo bool, profile semaProfileFlags, skipframes int, reason waitReason) {
gp := getg()
if gp != gp.m.curg {
throw("semacquire not on the G stack")
}
// Easy case.
if cansemacquire(addr) {
return
}
// Harder case:
// increment waiter count
// try cansemacquire one more time, return if succeeded
// enqueue itself as a waiter
// sleep
// (waiter descriptor is dequeued by signaler)
s := acquireSudog()
root := semtable.rootFor(addr)
t0 := int64(0)
s.releasetime = 0
s.acquiretime = 0
s.ticket = 0
if profile&semaBlockProfile != 0 && blockprofilerate > 0 {
t0 = cputicks()
s.releasetime = -1
}
if profile&semaMutexProfile != 0 && mutexprofilerate > 0 {
if t0 == 0 {
t0 = cputicks()
}
s.acquiretime = t0
}
for {
lockWithRank(&root.lock, lockRankRoot)
// Add ourselves to nwait to disable "easy case" in semrelease.
root.nwait.Add(1)
// Check cansemacquire to avoid missed wakeup.
if cansemacquire(addr) {
root.nwait.Add(-1)
unlock(&root.lock)
break
}
// Any semrelease after the cansemacquire knows we're waiting
// (we set nwait above), so go to sleep.
root.queue(addr, s, lifo)
goparkunlock(&root.lock, reason, traceEvGoBlockSync, 4+skipframes)
if s.ticket != 0 || cansemacquire(addr) {
break
}
}
if s.releasetime > 0 {
blockevent(s.releasetime-t0, 3+skipframes)
}
releaseSudog(s)
}release #
unc semrelease(addr *uint32) {
semrelease1(addr, false, 0)
}
func semrelease1(addr *uint32, handoff bool, skipframes int) {
root := semtable.rootFor(addr)
atomic.Xadd(addr, 1)
// Easy case: no waiters?
// This check must happen after the xadd, to avoid a missed wakeup
// (see loop in semacquire).
if root.nwait.Load() == 0 {
return
}
// Harder case: search for a waiter and wake it.
lockWithRank(&root.lock, lockRankRoot)
if root.nwait.Load() == 0 {
// The count is already consumed by another goroutine,
// so no need to wake up another goroutine.
unlock(&root.lock)
return
}
s, t0 := root.dequeue(addr)
if s != nil {
root.nwait.Add(-1)
}
unlock(&root.lock)
if s != nil { // May be slow or even yield, so unlock first
acquiretime := s.acquiretime
if acquiretime != 0 {
mutexevent(t0-acquiretime, 3+skipframes)
}
if s.ticket != 0 {
throw("corrupted semaphore ticket")
}
if handoff && cansemacquire(addr) {
s.ticket = 1
}
readyWithTime(s, 5+skipframes)
if s.ticket == 1 && getg().m.locks == 0 {
// Direct G handoff
// readyWithTime has added the waiter G as runnext in the
// current P; we now call the scheduler so that we start running
// the waiter G immediately.
// Note that waiter inherits our time slice: this is desirable
// to avoid having a highly contended semaphore hog the P
// indefinitely. goyield is like Gosched, but it emits a
// "preempted" trace event instead and, more importantly, puts
// the current G on the local runq instead of the global one.
// We only do this in the starving regime (handoff=true), as in
// the non-starving case it is possible for a different waiter
// to acquire the semaphore while we are yielding/scheduling,
// and this would be wasteful. We wait instead to enter starving
// regime, and then we start to do direct handoffs of ticket and
// P.
// See issue 33747 for discussion.
goyield()
}
}
}





